Our comprehensive analysis of social media conversations and mainstream media coverage about the banking industry, reveals a fascinating paradox in modern banking.
Banks are investing billions in advanced technologies. Yet customers consistently express a preference for human interaction over digital solutions. This contradiction shapes how financial institutions approach technology transformation in 2025 and beyond.
Through extensive social listening and media monitoring, we identified key banking technology trends driving industry discussions:
- AI and Automation
- Super App Banking
- Neobanking Evolution
- Cloud and Core Modernisation
- Cybersecurity and Operational Resilience
- Data Foundations and Governance
- Tech Talent Transformation
- Sustainable, ESG-Driven Innovation
- Blockchain in Banking
- The Human Connection in Banking
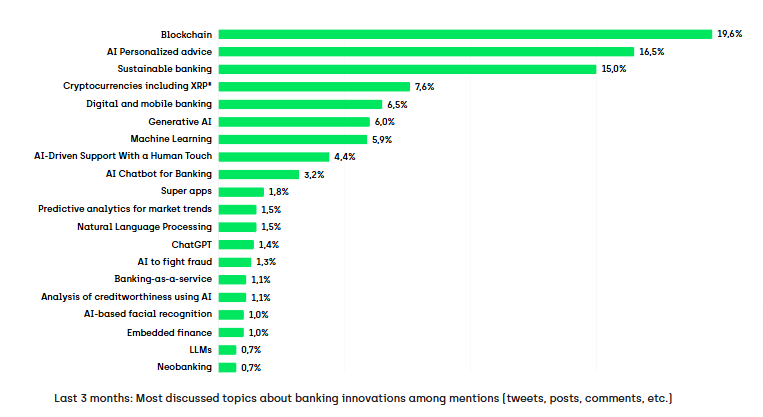
Source: Onclusive Banking Industry Scan
Interestingly, while blockchain technology generates the most discussion volume in our analysis, its practical impact has been more modest than anticipated. This disconnect between discussion and implementation highlights regulatory challenges, interoperability problems, and misaligned expectations about blockchain’s capabilities in banking.
Key Takeaways – Banking Technology Trends
- AI and automation are reshaping banking – from fraud detection to customer service, AI is the single biggest technology driver in the industry.
- Super apps are redefining customer expectations, combining financial services with lifestyle features in one platform.
- Neobanks continue to disrupt, offering digital-first experiences, though profitability and customer trust remain challenges.
- Blockchain generates more buzz than adoption, with banks still cautious about large-scale implementation.
- Cybersecurity is a top priority, as rising digital adoption increases the risk of fraud and data breaches.
- Cloud and core modernisation are accelerating, helping banks move away from inflexible legacy systems.
- ESG and sustainability are now central, with banks adopting technology to support green finance and transparent reporting.
- The human connection remains critical, as customers still expect personal support alongside digital services.
1. AI and Automation: The New Brain of Banking
AI is the single biggest change in bank technology trends today. Banks are deploying AI for fraud detection, customer service, and process automation, making it one of the most transformative forces in the industry. From chatbots that improve customer experience to advanced machine learning models detecting anomalies in real time, AI is already reshaping how banks operate.
Banks are also moving beyond small pilots and beginning to embed AI into enterprise-wide strategies. According to Deloitte, more than three-quarters of banks plan to increase investments in data management and cloud consumption to advance their generative AI initiatives. This highlights the urgency for institutions to scale their AI capabilities rather than experiment in silos.
The opportunity is enormous, but it requires cultural and organisational change. McKinsey argues that banks must become “AI-first institutions,” embedding AI across the enterprise rather than experimenting with isolated use cases. Only then can they unlock meaningful improvements in productivity, efficiency, and customer experience.
For banks, the message is clear: AI is no longer optional, it’s a competitive necessity.
Generative AI Changes Everything
Among the most significant bank technology trends are smart AI systems that outperform traditional rule-based programs. They can understand and create content like humans do.
- BBVA built a GPT Store with over 2,900 custom tools. This shows how banks can use AI across their entire business.
- JPMorgan Chase created the ‘LLM Suite’ for data analysis and market predictions. They also built IndexGPT to help customers analyze financial markets. The system processes huge amounts of market data and research reports.
- Morgan Stanley uses AI to help financial advisors find research for clients quickly. This makes complex financial information easier to understand.
- Barclays and NatWest invested heavily in AI governance. They created special committees to oversee AI use safely. This shows how important proper AI management is.
AI in Back Office Operations
Goldman Sachs uses AI to review documents automatically. This work used to take lawyers many hours. Now AI does it in minutes. And Deutsche Bank focuses on operational efficiency. Their AI systems process trade finance documents automatically. Processing time dropped from hours to minutes.

2. Super Apps: One Platform for Every Need
Modern banking technology lets banks serve millions of customers with personalized experiences. Our social listening analysis shows customers want banking integrated into their daily activities.
Super App Banking: One App for Everything
Traditional banking apps only do financial tasks. Super apps do much more. Users can message friends, order food, and transfer money all in one place.
Our analysis of social media shows Cash App, Revolut, and Grab lead super app banking discussions. These platforms prove that combining services creates value for users.
WeChat started as a messaging app. Now over one billion users pay bills, book appointments, and manage money through it. This seamless integration is what traditional banks struggle to match.
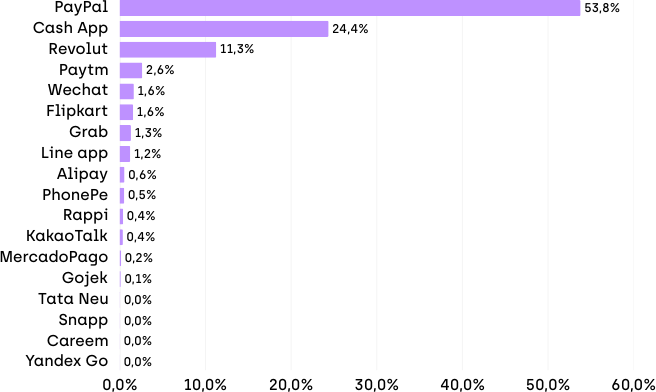
Success Stories Around the World
- Asian markets lead in super app development. Grab saw that many Southeast Asian users didn’t have bank accounts. So they created GrabPay to serve this market.
- Alipay grew from Alibaba’s shopping sites. Now it offers investments, insurance, and lifestyle services. It even has a credit scoring system called Sesame Credit.
- In Latin America, Rappi started with food delivery. They then added financial services through RappiPay. This shows how apps must adapt to local markets and payment habits.
Super apps see more than just transactions. They track shopping patterns, travel habits, and social interactions. This data helps them offer personalized services. For example, if you order food delivery often during work, they might offer a dining rewards credit card.
3. Cloud and Core Modernisation: Building the Digital Backbone
Among the most significant bank technology trends is the move from outdated legacy systems to flexible, cloud-based platforms that enable speed, scale and innovation. Cloud technology has evolved from being a cost-saving tool to a strategic advantage, allowing banks to move faster, scale more efficiently and integrate seamlessly with fintech partners.
- Open banking initiatives are accelerating this transformation. By adopting API-first designs, banks are shifting from closed systems to open platforms where third-party developers can safely build new services. This creates new revenue streams and enables banks to expand beyond traditional channels through fintech partnerships.
- The rise of embedded finance takes this even further. Payments, loans and insurance are now integrated into shopping sites, ride-sharing apps and digital marketplaces. Banks are extending their reach into customers’ daily lives, competing not just with other financial institutions but also with technology companies.
- Modernisation also means addressing decades-old infrastructure. Many banks still rely on core systems built in the 1970s, which consume 70 to 80 percent of IT budgets just to maintain. Today, banks are breaking these monolithic systems into modular microservices that can be updated independently. This allows for faster feature launches and lower risk when making changes.
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions now handle functions from payments to regulatory reporting, offering cutting-edge features without the cost of internal development. Combined with multi-cloud strategies that prevent dependency on a single vendor, banks are optimising performance, resilience and compliance across geographies.
- Together, cloud adoption and core modernisation form the digital backbone of the banking sector. They enable innovation, compliance and long-term competitiveness.
4. Cybersecurity: Defending Trust in a Digital World
AI is the single biggest change in banking technology today. Banks are deploying AI for fraud detection, customer service, and process automation, making it one of the most transformative forces in the industry. From chatbots that improve customer experience to advanced machine learning models detecting anomalies in real time, AI is already reshaping how banks operate.
Banks are also moving beyond small pilots and beginning to embed AI into enterprise-wide strategies. According to Deloitte, more than three-quarters of banks plan to increase investments in data management and cloud consumption to advance their generative AI initiatives. This highlights the urgency for institutions to scale their AI capabilities rather than experiment in silos.
The opportunity is enormous, but it requires cultural and organisational change. McKinsey argues that banks must become “AI-first institutions,” embedding AI across the enterprise rather than experimenting with isolated use cases. Only then can they unlock meaningful improvements in productivity, efficiency, and customer experience.
For banks, the message is clear: AI is no longer optional, it’s a competitive necessity.
5. Data Foundations: Building the Backbone of Banking AI
Good data quality supports all advanced banking technologies. Without reliable data, AI systems fail and regulatory compliance breaks down. This makes data management a critical priority for every bank.
Modern data platforms track information from start to finish. They monitor data quality automatically and fix problems before they affect business operations. Machine learning algorithms optimize data storage and processing.
Banks need “AI-ready” data to power their machine learning systems. This means data must be clean, complete, and easily accessible. Many banks struggle because their data sits in separate systems that don’t communicate.
New techniques let banks analyze sensitive data without compromising customer privacy. Methods like differential privacy add mathematical “noise” to data sets. This protects individual privacy while still allowing useful analysis.
6. Tech Talent: The New Skills Banks Need
Banking transformation needs new skills that traditional structures can’t support. The industry faces a critical shortage of professionals who understand both banking and modern technology.
Training programs help existing employees learn digital skills while preserving their banking knowledge. Leading banks are adopting software engineering practices like continuous integration and automated testing to launch features quickly while maintaining security.
Partnerships with fintech companies and universities provide access to specialized knowledge. Many banks now embed technology experts within business teams rather than keeping them separate.
7. ESG Innovation: Banking for a Sustainable Future
ESG in banking refers to the integration of environmental, social, and governance principles into financial services, from green finance to transparent reporting.
Real Sustainability Initiatives
- NatWest Group promised £100 billion in climate funding by 2025. They stopped lending to new coal projects. They also launched green mortgages with better rates for energy-efficient homes.
- However, NatWest faced criticism from farmers. Their app suggested reducing beef and dairy consumption to lower carbon footprints. This shows how sustainability efforts can create controversy.
- Bank of America committed $1 trillion by 2030 to support clean energy transition. This includes financing clean technology companies and creating new environmental financial products.
- UniCredit in Italy leads with investment funds focused on clean energy transition.
Real Change vs. Marketing
Genuine sustainability innovation changes core banking processes. For example, banks integrate environmental risk assessment into standard credit decisions. Leading banks get independent verification of their environmental claims. They set measurable targets and report progress regularly.
8. Neobanks: Digital-First Banking at a Crossroads
Neobanks are fully digital banks that operate without physical branches, offering mobile-first experiences at lower cost. Digital-only banks changed how financial services work. Our social media analysis shows neobanks like Monzo, N26, Revolut, and Chime transformed basic banking. But they face big profitability challenges.
The Neobank Advantage
Digital banks don’t need physical branches. This cuts costs significantly. They can offer lower fees or free services. Their modern technology, built from scratch, enables rapid innovation and smooth digital experiences.
Nubank in Brazil shows this success. They serve over 70 million customers by using technology to reach people without traditional bank accounts.
Revolut and N26 expanded quickly across Europe. They offer multi-currency accounts and commission-free stock trading. Traditional banks struggled to match these features.
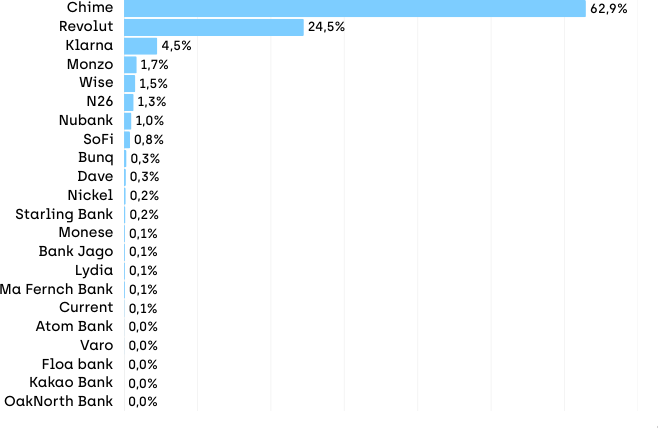
Profitability Problems
Many digital banks struggle to make money and their low-fee models need massive scale to work. Customer acquisition costs stay high. And competition intensified as traditional banks improved their digital services.
Many customers use neobanks as secondary accounts. They keep their main relationship with traditional banks. This limits neobank growth and profitability.
However, the neobank sector is maturing. The early phase of rapid growth is ending and now there’s more focus on sustainable business models and actual profitability. This means consolidation, specialization, and partnership models.
| Advantages of Neobanks | Challenges of Neobanks |
| Fully digital-first, mobile-native experiences designed for younger, tech-savvy users | Profitability remains a major hurdle, with many neobanks still operating at a loss |
| Lower operating costs due to the absence of physical branches | Regulatory scrutiny is increasing as neobanks grow and handle more customer funds |
| Rapid growth and scaling, with global success stories like Nubank and Revolut | Building customer trust can be harder without the established reputation of traditional banks |
| Innovative services and flexible product offerings tailored to niche audiences | Facing fierce competition from traditional banks adopting digital tools and other fintech players |
9. Blockchain in Banking: Hype vs Adoption
Blockchain in banking refers to distributed ledger technology used for secure transactions, transparency, and potential cost reduction, although adoption remains limited.
Despite our analysis showing that blockchain dominates industry conversations, blockchain’s real-world impact in banking has been more modest than anticipated. Banks have explored creating tokenized versions of traditional assets (like bonds and currencies) but the shift toward blockchain-based trading has moved more slowly than expected, with fragmentation and regulatory uncertainty cited by leaders at institutions like Citibank as key barriers.
Most activity remains confined to pilot projects and niche use cases such as cross-border payments, trade finance, and digital identity verification. Regulatory uncertainty, high implementation costs, and system interoperability continue to slow down broader adoption.
For now, blockchain in banking remains a story of potential rather than reality. While discussions remain high, few institutions have introduced the technology at scale, underscoring the persistent gap between hype and tangible change.
10. The Human Connection: Why People Still Matter in Banking
The human connection in banking refers to the personal relationships, trust, and reassurance customers expect alongside digital services.
Our analysis shows that even as banks invest billions in advanced technologies, customers consistently express a preference for personal support when it matters most. This paradox highlights that technology should enhance, not replace, the human element of financial services.
Branches, call centres, and personal advisers remain vital for resolving complex issues, providing financial guidance, and building long-term trust. While AI and digital tools streamline day-to-day banking, customers still want the option of speaking with a human during moments of stress, uncertainty, or major financial decisions.
For banks, the challenge is not choosing between digital and human service, but creating a hybrid model where technology provides speed and scale, while people deliver empathy and connection. Those that get this balance right will build stronger loyalty and competitive advantage in the years ahead.
Conclusion: From Cost Centre to Innovation Powerhouse
Our analysis shows that bank technology trends have shifted from being seen as a cost centre to becoming a strategic advantage, shaping how banks will compete through 2030. Yet the paradox remains: while digital transformation accelerates, customers continue to value human connection alongside technology.
At Onclusive, our analysis of millions of social and media conversations shows how these trends are shaping the future of banking. For financial institutions, understanding and acting on these technology shifts is no longer optional; it’s the key to building trust, resilience, and competitive advantage in the decade ahead.
Executive Implications
- Technology transformation needs comprehensive change management. It must address culture, processes, and infrastructure together.
- Our research and analysis revealed a paradox. Customers often prefer human interaction despite significant technology investments. This shows the importance of using AI and technology to enhance rather than replace personal connections.
- Good data quality and governance support all advanced technologies. Cloud computing and API systems create the flexibility needed for rapid innovation and partnerships.
- Banks that view technology as an innovation driver rather than just a cost will emerge as leaders. Those that fail to embrace transformation risk becoming irrelevant.
The Path Forward
To stay competitive, banks must use high-performance social listening and media monitoring tools to:
- Detect industry trends quickly
- Anticipate consumer behavior changes
- Identify new opportunities before competitors
Continuous monitoring of social media conversations, industry news, and competitor moves is now crucial for navigating the changing banking landscape.
The future belongs to banks that successfully balance technological innovation with human-centered service. They create sustainable competitive advantages through strategic technology deployment. This enhances rather than replaces the personal relationships that customers still value.
About This Research
This article uses comprehensive social listening and media analysis data from Onclusive’s Banking Industry Scan. It examines technology trend discussions across social media platforms and mainstream media coverage.
